Bybit Identifies 16 Blockchains Capable of Freezing or Restricting User Funds
- Bybit’s Lazarus Security Lab analyzed 166 blockchains, finding 16 with the technical ability to freeze or restrict user funds
- Networks like BNB Chain, VeChain, and Sui were identified with fund-freezing mechanisms built into their code
- Cosmos ecosystem could potentially enable freezing with minor protocol changes
- The report raises decentralization concerns across blockchain networks
- Comes months after Bybit’s $1.5B hack, where partners froze over $42.9M in exploited funds
A new report by Bybit’s Lazarus Security Lab has revealed that 16 blockchain networks possess the technical capacity to freeze or restrict user funds, challenging the perception that all blockchain systems are fully decentralized.
The findings, released on Tuesday, came after the lab analyzed 166 different blockchain networks using a mix of AI-driven analysis and manual verification. The goal was to assess how various blockchain designs manage fund control and whether any systems allow entities to block transactions or lock funds at the protocol level.
Among the blockchains identified, Binance-backed BNB Chain was singled out as one of the most prominent examples, with freezing functions hardcoded directly into its source code. Similarly, the Cosmos chain was flagged as one of 19 networks that could easily introduce a freezing mechanism with minimal protocol modifications.
Three Mechanisms for Fund Freezing
Bybit’s research identified three primary methods that blockchain systems use to enable freezing at the protocol level.
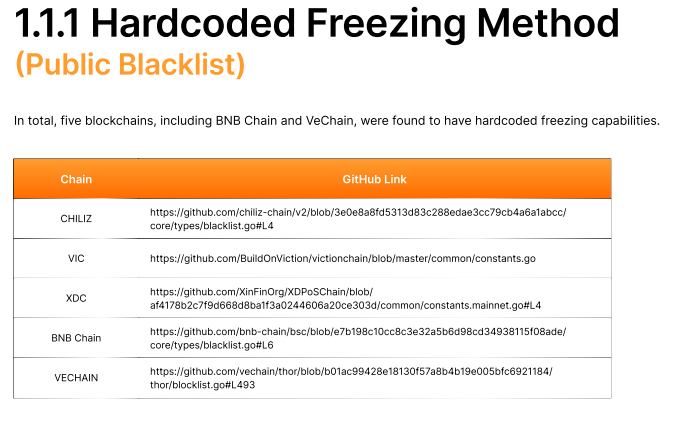
- Hardcoded Freezing or Public Blacklists:
These systems have freezing functions embedded in their base code, enabling administrators or developers to block specific wallets directly.
Blockchains using this method include BNB Chain, VeChain, Chiliz, Viction, and XinFin’s XDC Network.
- Configuration File-Based Freezing:
About ten networks rely on local configuration files such as YAML, ENV, or TOML to restrict user funds. These files are typically accessible only to validators or core developers, giving them significant control over fund access.
Aptos, Eos, and Sui were among the blockchains categorized under this model. - Onchain Smart Contract-Based Freezing:
The Heco Chain (Huobi Eco Chain) was found to be the only blockchain using a smart contract-driven blacklist, allowing it to manage restrictions directly through programmable contracts on the network.
These findings highlight that even within systems marketed as decentralized, administrative control layers still exist, allowing certain actors to interfere with user funds under specific conditions.
Potential Freezing in the Cosmos Ecosystem
The report also examined the Cosmos ecosystem, identifying that it could enable similar fund-freezing capabilities with only minor protocol updates.
The Lazarus team noted that Cosmos uses module accounts — specialized accounts governed by logic rather than private keys — that could theoretically be modified to block transactions.
Although no Cosmos-based chains currently use this feature for censorship or restriction, the report warned that implementing such capabilities would only require a hard fork and small code changes, likely in the anteHandler file.
Bybit’s researchers cautioned that while these functions are sometimes implemented to prevent hacks or recover stolen funds, they also pose serious decentralization and censorship risks.
A Centralization Debate Rekindled
The findings from Bybit’s Lazarus Security Lab add fuel to the ongoing debate about how decentralized most blockchains truly are.
As more networks integrate emergency controls, compliance modules, and admin-level privileges, questions arise about whether the industry is drifting toward centralized oversight disguised as user protection.
While these features can help mitigate security risks, they also enable entities to override the trustless nature of blockchain systems — something that goes against the core philosophy of decentralization.
Context: Bybit’s Own $1.5B Hack
The timing of this report is notable, coming just months after Bybit suffered a $1.5 billion cold wallet hack, one of the largest in crypto history.
In that incident, Bybit collaborated with industry partners like Circle, Tether, THORchain, and Bitget to freeze $42.9 million in stolen assets. Meanwhile, mETH Protocol managed to recover around $43 million worth of compromised tokens.
While the response showcased the effectiveness of coordinated security measures, it also demonstrated the extent of centralized control mechanisms available within supposedly decentralized systems.



